javascript full guid
JavaScript is a dynamically typed language. Because data type will automatically assigned at the time of compilation or code execution.
Jb b ap function return kra gha to variable ma store kra sakty ha sirf console log say ni kr sakty
return
//datatypes are based on memory allocation
Primitive datatypes-> call by value (string,number,boolean,null,undefined,BigInt,symbol) ->Stack memory
Reference/Non primitive data types -> call by reference ( array,object, function) -> heap memory
JavaScript is a dynamically typed language. This means that you don't need to specify the data type of a
variable when you declare it.
01_variables.js
const accountId = 144553
let accountEmail = "hitesh@google.com"
var accountPassword = "12345"
accountCity = "Jaipur"
let accountState;
// accountId = 2 // not allowed
accountEmail = "hc@hc.com"
accountPassword = "21212121"
accountCity = "Bengaluru"
console.log(accountId);
/*
Prefer not to use var
because of issue in block scope and functional scope
*/
console.table([accountId, accountEmail, accountPassword, accountCity, accountState])
02_dataTypes.js
"use strict"; // treat all JS code as newer version
// alert( 3 + 3) // we are using nodejs, not browser
console.log(3
+
3) // code readability should be high
console.log("Hitesh")
let name = "hitesh"
let age = 18
let isLoggedIn = false
let state;
// number => 2 to power 53
// bigint
// string => ""
// boolean => true/false
// null => standalone value
// undefined =>
// symbol => unique
// object
console.log(typeof undefined); // undefined
console.log(typeof null); // object
03_conversionOperation.js
let score = "hitesh"
//console.log(typeof score);
//console.log(typeof(score));
let valueInNumber = Number(score)
//console.log(typeof valueInNumber);
//console.log(valueInNumber);
// "33" => 33
// "33abc" => NaN
// true => 1; false => 0
let isLoggedIn = "hitesh"
let booleanIsLoggedIn = Boolean(isLoggedIn)
// console.log(booleanIsLoggedIn);
// 1 => true; 0 => false
// "" => false
// "hitesh" => true
let someNumber = 33
let stringNumber = String(someNumber)
// console.log(stringNumber);
// console.log(typeof stringNumber);
// *********************** Operations ***********************
let value = 3
let negValue = -value
// console.log(negValue);
// console.log(2+2);
// console.log(2-2);
// console.log(2*2);
// console.log(2**3);
// console.log(2/3);
// console.log(2%3);
let str1 = "hello"
let str2 = " hitesh"
let str3 = str1 + str2
// console.log(str3);
// console.log("1" + 2);
// console.log(1 + "2");
// console.log("1" + 2 + 2);
// console.log(1 + 2 + "2");
// console.log( (3 + 4) * 5 % 3);
// console.log(+true);
// console.log(+"");
let num1, num2, num3
num1 = num2 = num3 = 2 + 2
let gameCounter = 100
++gameCounter;
console.log(gameCounter);
// link to study
// https://tc39.es/ecma262/multipage/abstract-operations.html#sec-type-conversion
04_comparision.js
// console.log(2 > 1);
// console.log(2 >= 1);
// console.log(2 < 1);
// console.log(2 == 1);
// console.log(2 != 1);
// console.log("2" > 1);
// console.log("02" > 1);
console.log(null > 0);
console.log(null == 0);
console.log(null >= 0);
console.log(undefined == 0);
console.log(undefined > 0);
console.log(undefined < 0);
// ===
console.log("2" === 2);
datatypes-summary.js
// Primitive
// 7 types : String, Number, Boolearn, null, undefined, Symbol, BigInt
const score = 100
const scoreValue = 100.3
const isLoggedIn = false
const outsideTemp = null
let userEmail;
const id = Symbol('123')
const anotherId = Symbol('123')
console.log(id === anotherId);
// const bigNumber = 3456543576654356754n
// Reference (Non primitive)
// Array, Objects, Functions
const heros = ["shaktiman", "naagraj", "doga"];
let myObj = {
name: "hitesh",
age: 22,
}
const myFunction = function(){
console.log("Hello world");
}
console.log(typeof anotherId);
// https://262.ecma-international.org/5.1/#sec-11.4.3
data type typeof operator
Thank you sir for your guidance and hard work here is your gift
* Premitive Datatypes
Type typeof
i) Number number
ii) String string
iii) Boolean boolean
iv) Bigint bigint
v) Symbol symbol
vi) Null object
vii) Undefined undefined
* Non-Premitive OR Referance OR Object datatype
Type typeof
i) Object object
ii) Array object
iii) Function function(object)
This is my research and output if anythig is wrong please feel proud to reply me
Stack and Heap memory in javascript
let youtubename="Developer";
let myname=youtubename;
myname="Website";
console.log(youtubename);
console.log(myname);
let userone={
name:"ALI",
age:21
}
let usertwo=userone;
usertwo.name="RAO";
console.log(userone.name);
console.log(usertwo.name);
05_strings.js
const name = "hitesh"
const repoCount = 50
// console.log(name + repoCount + " Value");
console.log(`Hello my name is ${name} and my repo count is ${repoCount}`);
const gameName = new String('hitesh-hc-com')
// console.log(gameName[0]);
// console.log(gameName.__proto__);
// console.log(gameName.length);
// console.log(gameName.toUpperCase());
console.log(gameName.charAt(2));
console.log(gameName.indexOf('t'));
const newString = gameName.substring(0, 4)
console.log(newString);
const anotherString = gameName.slice(-8, 4)
console.log(anotherString);
const newStringOne = " hitesh "
console.log(newStringOne);
console.log(newStringOne.trim());
const url = "https://hitesh.com/hitesh%20choudhary"
console.log(url.replace('%20', '-'))
console.log(url.includes('sundar'))
console.log(gameName.split('-'));
JavaScript String Methods
06_nums_and_math.js
const score = 400
// console.log(score);
const balance = new Number(100)
// console.log(balance);
// console.log(balance.toString().length);
// console.log(balance.toFixed(1));
const otherNumber = 123.8966
// console.log(otherNumber.toPrecision(4));
const hundreds = 1000000
// console.log(hundreds.toLocaleString('en-IN'));
// +++++++++++++ Maths +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
// console.log(Math);
// console.log(Math.abs(-4));
// console.log(Math.round(4.6));
// console.log(Math.ceil(4.2));
// console.log(Math.floor(4.9));
// console.log(Math.min(4, 3, 6, 8));
// console.log(Math.max(4, 3, 6, 8));
console.log(Math.random());
console.log((Math.random()*10) + 1);
console.log(Math.floor(Math.random()*10) + 1);
const min = 10
const max = 20
console.log(Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min)
02_basics
01_arrays.js
// array
const myArr = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
const myHeors = ["shaktiman", "naagraj"]
const myArr2 = new Array(1, 2, 3, 4)
// console.log(myArr[1]);
// Array methods
// myArr.push(6)
// myArr.push(7)
// myArr.pop()
// myArr.unshift(9)
// myArr.shift()
// console.log(myArr.includes(9));
// console.log(myArr.indexOf(3));
// const newArr = myArr.join()
// console.log(myArr);
// console.log( newArr);
// slice, splice
console.log("A ", myArr);
const myn1 = myArr.slice(1, 3)
console.log(myn1);
console.log("B ", myArr);
const myn2 = myArr.splice(1, 3)
console.log("C ", myArr);
console.log(myn2);
02_array.js
const marvel_heros = ["thor", "Ironman", "spiderman"]
const dc_heros = ["superman", "flash", "batman"]
// marvel_heros.push(dc_heros)
// console.log(marvel_heros);
// console.log(marvel_heros[3][1]);
// const allHeros = marvel_heros.concat(dc_heros)
// console.log(allHeros);
const all_new_heros = [...marvel_heros, ...dc_heros]
// console.log(all_new_heros);
const another_array = [1, 2, 3, [4, 5, 6], 7, [6, 7, [4, 5]]]
const real_another_array = another_array.flat(Infinity)
console.log(real_another_array);
console.log(Array.isArray("Hitesh"))
console.log(Array.from("Hitesh"))
console.log(Array.from({name: "hitesh"})) // interesting
let score1 = 100
let score2 = 200
let score3 = 300
console.log(Array.of(score1, score2, score3));
04_objects.js
// const tinderUser = new Object()
const tinderUser = {}
tinderUser.id = "123abc"
tinderUser.name = "Sammy"
tinderUser.isLoggedIn = false
// console.log(tinderUser);
const regularUser = {
email: "some@gmail.com",
fullname: {
userfullname: {
firstname: "hitesh",
lastname: "choudhary"
}
}
}
// console.log(regularUser.fullname.userfullname.firstname);
const obj1 = {1: "a", 2: "b"}
const obj2 = {3: "a", 4: "b"}
const obj4 = {5: "a", 6: "b"}
// const obj3 = { obj1, obj2 }
// const obj3 = Object.assign({}, obj1, obj2, obj4)
const obj3 = {...obj1, ...obj2}
// console.log(obj3);
const users = [
{
id: 1,
email: "h@gmail.com"
},
{
id: 1,
email: "h@gmail.com"
},
{
id: 1,
email: "h@gmail.com"
},
]
users[1].email
// console.log(tinderUser);
// console.log(Object.keys(tinderUser));
// console.log(Object.values(tinderUser));
// console.log(Object.entries(tinderUser));
// console.log(tinderUser.hasOwnProperty('isLoggedIn'));
const course = {
coursename: "js in hindi",
price: "999",
courseInstructor: "hitesh"
}
// course.courseInstructor
const {courseInstructor: instructor} = course
// console.log(courseInstructor);
console.log(instructor);
// {
// "name": "hitesh",
// "coursename": "js in hindi",
// "price": "free"
// }
[
{},
{},
{}
]
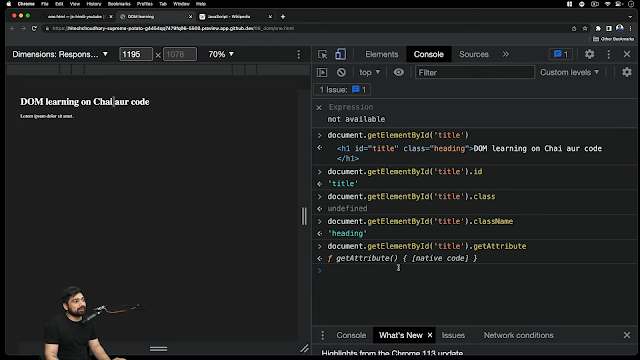
DOM introduction in javascript
console.log(window)
console.log(window.document)
console.dir(document)











Comments
Post a Comment